Interrelationship Between Visceral fat, Inflammation And Metabolic Syndrome!
The Cluster Of Visceral Fat, Inflammation And Metabolic Syndrome!
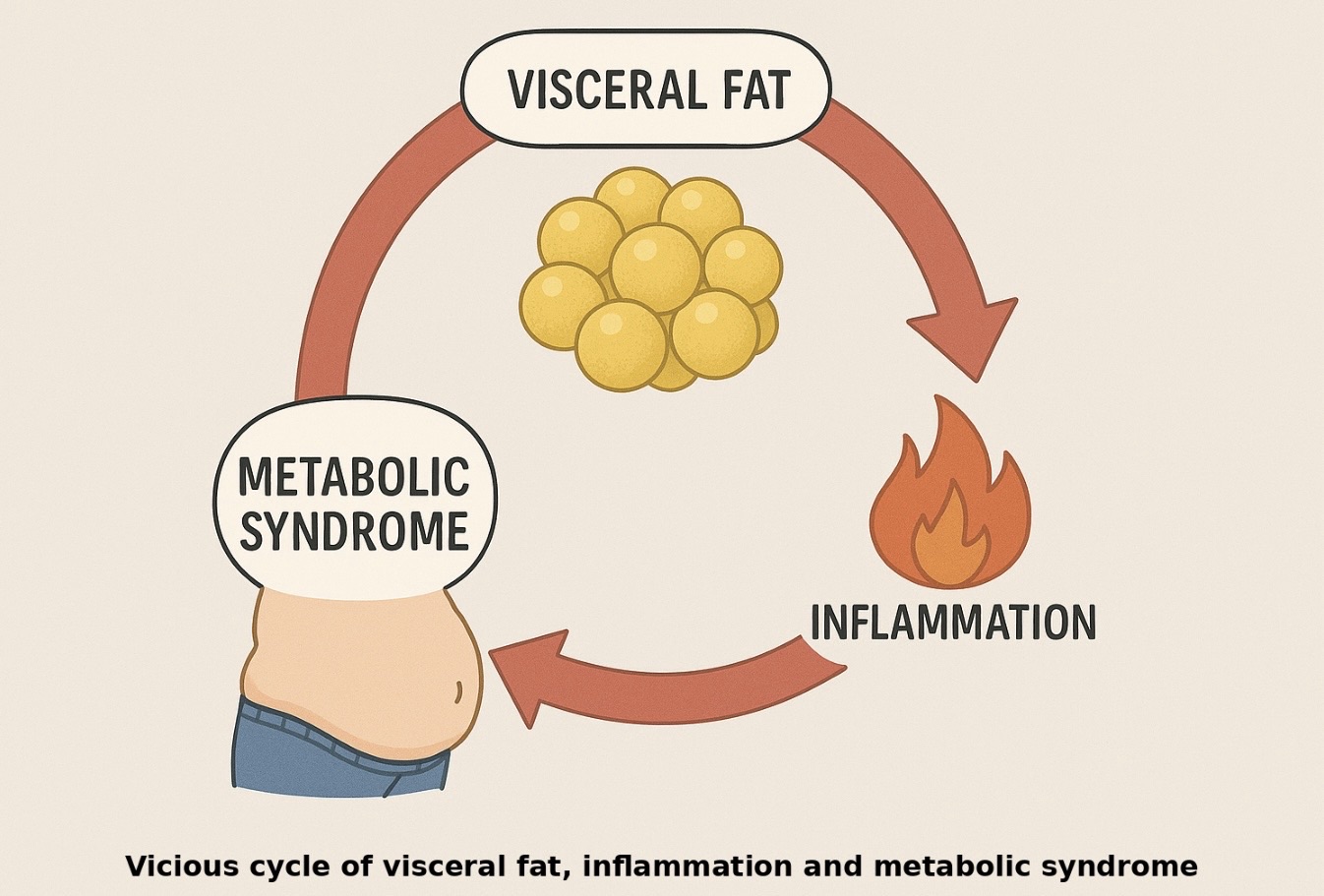
The interrelationship between inflammation, excess visceral fat, and metabolic syndrome is central to understanding many chronic diseases, especially those involving the heart, blood sugar regulation, and lipid balance. Here’s a clear breakdown of how these three are interconnected.
***
Visceral Fat as a Source of Chronic Inflammation
Visceral fat (fat stored around internal organs, especially in the abdomen) is biologically active.
It secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as:
TNF-α (Tumour Necrosis Factor alpha)
IL-6 (Interleukin-6)
These compounds create a state of chronic low-grade inflammation in the body, unlike the acute inflammation seen in infections or injuries.
***
Inflammation Promotes Insulin Resistance
Chronic inflammation interferes with insulin signalling pathways.
Cytokines like TNF-α disrupt insulin receptors, making body cells less responsive to insulin.
This is a key mechanism in the development of insulin resistance, a hallmark of metabolic syndrome.
***
Metabolic syndrome is cluster of following conditions and it creates hypertension, type 2 diabetes, heart disease, strokes, and also diseases like fatty liver and PCOS in ladies and increases the risk of developing some cancers.
Metabolic Syndrome and Its Inflammatory Roots
It also increases the risk of development of fatty liver disease and in women, polycystic ovarian syndrome or PCOS.
These conditions include:
High waist circumference (central obesity / visceral fat)
High blood pressure
Insulin resistance (high fasting blood sugar)
High triglycerides
Low HDL (good) cholesterol
Chronic inflammation exacerbates these conditions and metabolic syndrome and they in turn fuel more inflammation, creating a vicious cycle.
***
Diagnostic Clues
Assessment of visceral fat
It can be done by measuring the waist circumference and by using the body composition scans.
Waist circumference of over 37 inches (94 cm) in Indian men and above 31.5 inches (80 cm) indicate presence of excess visceral fat in the abdomen.
CRP (C-reactive protein) is elevated due to inflammation.
Elevated hs-CRP (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein) is a marker of inflammation linked to metabolic syndrome.
Levels of hs-CRP above of 1 mg/L indicate moderate inflammation and over 3 mg/L indicates significant levels of inflammation and indicates increased risk of developing diabetes and heart disease.
***
Breaking the Vicious Cycle
Losing weight helps reverse abdominal obesity and this helps reduce inflammation.
Adapting an anti inflammatory diet made up of whole grain cereals and pulses, fruits and vegetables, low fat milk and sea fish if possible (a diet rich in fiber, antioxidants and lean protein and omega-3 fats) helps.
Cardiovascular exercise helps reduce visceral fat and inflammation.
Medications like metformin or statins prescribed by doctors may help in some cases.
Also read the articles ‘Abdominal Obesity, Diabetes And Heart Disease’, ‘Acute And Chronic Inflammation’ and ‘Metabolic Syndrome’.