Posts Shortcodes
You can show the posts with Porto Blog, Porto Recent Posts shortcodes.
Recent
Timeline
June 2025
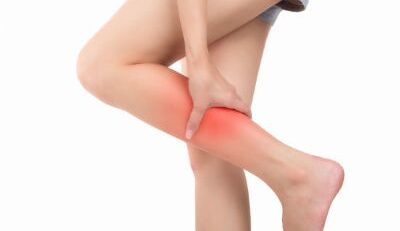
Muscle Cramps, A Common Problem!
Sudden, Painful Spasms Of Muscles!
Muscle cramps is a sudden and very painful condition that most people have experienced some time or another in their lives.
Muscle cramps means a sudden, involuntary and very painful contraction of a muscle or a group of muscles that actually freezes a person in that position, making it very difficult to move.
Such cramps are more common in the calf muscles and occur more often at night, but cramps can occur in other muscles and anytime of the day too.
Common Causes of Muscle Cramps
Dehydration:
Loss of fluids through sweating or inadequate intake of water can disturb electrolyte balance.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Low levels of magnesium, potassium, calcium, or sodium can trigger cramps.
Overuse or Strain:
Prolonged exercise or muscle fatigue can lead to cramps, especially in hot weather.
Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Holding one position too long, particularly with legs bent or crossed.
Poor Circulation:
Reduced blood flow to muscles, especially in peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Nerve Compression:
Spinal nerve issues (like lumbar stenosis) can cause cramping pain, especially in legs.
Medications:
Diuretics, statins, or certain blood pressure medications can cause cramps.
Medical Conditions:
Diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, or liver cirrhosis.
Pregnancy:
Common in the second and third trimesters due to changes in circulation and pressure on nerves.
Treatment and Relief
Immediate Relief:
Stretching and Massage
Gently stretch (e.g., flex the foot for a calf cramp) and massage the cramped muscle
Apply Heat or Cold:
Use heat (e.g., warm towel or heating pad) for tight muscles.
Apply ice packs for soreness of muscles after that comes after the cramp.
Hydration
Drink adequate water or an electrolyte drink, especially after sweating or exercise.
Long-Term Management & Prevention
Stay Well Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Correct Electrolyte Deficiencies:
Eat foods rich in potassium (bananas, oranges), magnesium (nuts, legumes), and calcium (milk, leafy greens).
Stretch Regularly:
Gentle stretches before bed, especially if you get night cramps.
Adjust Exercise Routine:
Avoid overtraining and allow time for rest and muscle recovery.
Use Proper Footwear:
Use supportive shoes, especially if you’re on your feet a lot.
Medication Review:
Consult your doctor if cramps persist, or if they started after a new medication.
Also read the article ‘Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!’ on this website.
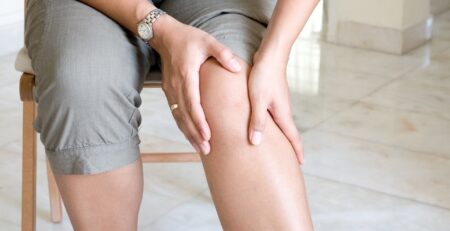
Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Occasional Fatigue And Pain In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Many regular walkers experience days of weakness, fatigue or heaviness and pain in legs when they wake up in the morning and want to go out for their regular walk.
It could happen due to a few reasons, mostly not too serious.
Sweating heavily on long walks especially on warm and humid days and not drinking enough water can cause dehydration which can cause interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles causing this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Same kind of interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles can occur due to the deficiency of magnesium, potassium or calcium and can cause this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Repetitive use of quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles in walking sometimes can cause building up of lactic acid in these muscle groups or can cause micro tears in muscles, causing heaviness or drained feeling in these muscles. This happens more often if you have increased the intensity or duration of walks or have added some upward slopes in walks recently.
This can also happen if the muscles haven’t gotten enough time to recover from long walks or prolonged standing.
This can also happen if your shoes do not provide proper support to the arch of your feet or if the sole of your shoes have worn thin with long use, or you have been walking on hard surfaces, causing strain on your leg muscles, making them painful.
Pain in legs could also be caused by vertebral problems causing pressure on the nerves going down into the legs or due to some neurological diseases, but these pains are less likely to be temporary.
Preventive tips:
Drink ample water, more so in hot climates.
Use good quality walking shoes of a good brand.
Try walking on softer surfaces like on natural ground or lawns.
Lie on your bed with your legs elevated, preferably against a wall close to the bed, or on cushions or roll of a blanket, after a walk.
Have a rest day between walking days to allow the muscles to ‘recover’.
Include magnesium rich foods like pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, almonds, cashew nuts (in moderation if you’re watching your weight), brown rice, oats, black , lentils (masur, toor, mug, matki), chickpeas, soya, spinach and other green leafy vegetables, sea fish, in your food.
Happy walking to all!
Also read ‘Magical Health Benefits Of Walking’ and ‘Walking To Be Slim And Healthy’ on this website!
Grid
Muscle Cramps, A Common Problem!
Sudden, Painful Spasms Of Muscles!
Muscle cramps is a sudden and very painful condition that most people have experienced some time or another in their lives.
Muscle cramps means a sudden, involuntary and very painful contraction of a muscle or a group of muscles that actually freezes a person in that position, making it very difficult to move.
Such cramps are more common in the calf muscles and occur more often at night, but cramps can occur in other muscles and anytime of the day too.
Common Causes of Muscle Cramps
Dehydration:
Loss of fluids through sweating or inadequate intake of water can disturb electrolyte balance.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Low levels of magnesium, potassium, calcium, or sodium can trigger cramps.
Overuse or Strain:
Prolonged exercise or muscle fatigue can lead to cramps, especially in hot weather.
Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Holding one position too long, particularly with legs bent or crossed.
Poor Circulation:
Reduced blood flow to muscles, especially in peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Nerve Compression:
Spinal nerve issues (like lumbar stenosis) can cause cramping pain, especially in legs.
Medications:
Diuretics, statins, or certain blood pressure medications can cause cramps.
Medical Conditions:
Diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, or liver cirrhosis.
Pregnancy:
Common in the second and third trimesters due to changes in circulation and pressure on nerves.
Treatment and Relief
Immediate Relief:
Stretching and Massage
Gently stretch (e.g., flex the foot for a calf cramp) and massage the cramped muscle
Apply Heat or Cold:
Use heat (e.g., warm towel or heating pad) for tight muscles.
Apply ice packs for soreness of muscles after that comes after the cramp.
Hydration
Drink adequate water or an electrolyte drink, especially after sweating or exercise.
Long-Term Management & Prevention
Stay Well Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Correct Electrolyte Deficiencies:
Eat foods rich in potassium (bananas, oranges), magnesium (nuts, legumes), and calcium (milk, leafy greens).
Stretch Regularly:
Gentle stretches before bed, especially if you get night cramps.
Adjust Exercise Routine:
Avoid overtraining and allow time for rest and muscle recovery.
Use Proper Footwear:
Use supportive shoes, especially if you’re on your feet a lot.
Medication Review:
Consult your doctor if cramps persist, or if they started after a new medication.
Also read the article ‘Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!’ on this website.
Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Occasional Fatigue And Pain In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Many regular walkers experience days of weakness, fatigue or heaviness and pain in legs when they wake up in the morning and want to go out for their regular walk.
It could happen due to a few reasons, mostly not too serious.
Sweating heavily on long walks especially on warm and humid days and not drinking enough water can cause dehydration which can cause interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles causing this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Same kind of interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles can occur due to the deficiency of magnesium, potassium or calcium and can cause this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Repetitive use of quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles in walking sometimes can cause building up of lactic acid in these muscle groups or can cause micro tears in muscles, causing heaviness or drained feeling in these muscles. This happens more often if you have increased the intensity or duration of walks or have added some upward slopes in walks recently.
This can also happen if the muscles haven’t gotten enough time to recover from long walks or prolonged standing.
This can also happen if your shoes do not provide proper support to the arch of your feet or if the sole of your shoes have worn thin with long use, or you have been walking on hard surfaces, causing strain on your leg muscles, making them painful.
Pain in legs could also be caused by vertebral problems causing pressure on the nerves going down into the legs or due to some neurological diseases, but these pains are less likely to be temporary.
Preventive tips:
Drink ample water, more so in hot climates.
Use good quality walking shoes of a good brand.
Try walking on softer surfaces like on natural ground or lawns.
Lie on your bed with your legs elevated, preferably against a wall close to the bed, or on cushions or roll of a blanket, after a walk.
Have a rest day between walking days to allow the muscles to ‘recover’.
Include magnesium rich foods like pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, almonds, cashew nuts (in moderation if you’re watching your weight), brown rice, oats, black , lentils (masur, toor, mug, matki), chickpeas, soya, spinach and other green leafy vegetables, sea fish, in your food.
Happy walking to all!
Also read ‘Magical Health Benefits Of Walking’ and ‘Walking To Be Slim And Healthy’ on this website!
Walking Helps Improve Muscle Tone Too!
Effect Of Walking On Muscle Tone!
Many people imagine that walking does not help tone up body muscles.
But it isn’t true.
Walking does improve various lower body group of muscles and also the core muscles.
Walking is an excellent low-impact exercise that also helps tone and strengthen several key muscle groups, primarily in the lower body and core. Here are the muscles groups that are engaged and toned through regular walking:
Leg Muscles:
Quadriceps is the group of four muscles (Rectus femoris, Vastus lateralis, Vastus medialis and Vastus intermedius) in front of thighs, that helps flex the hip and extends the knee with each step.
Hamstrings is the group of three muscles (Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus and Semimembranosus) at the back of thighs that helps extend the thigh and flex the knee.
Calves have two muscles (Gastrocnemius and Soleus) that help us push-off while walking.
Tibialis anterior is the muscle in front of the lower leg that lifts the foot during the swing phase.
Glutes (Buttocks)
Gluteus maximus, Gluteus medius and Gluteus minimus are the muscles that help with hip extension and stabilisation of hip. Walking uphill, climbing stairs or brisk walking especially activates the glutes more intensely.
Hip Muscles
Hip Flexors (Iliopsoas, Rectus Femoris, Sartorius, Pectineus, Iliacus, Psoas Major) help lift the leg towards the chest and help us bend forward.
Hip Adductors (Adductor longus, Adductor brevis, Adductor magnus, Gracilis, and Pectineus), they help bring the leg towards the midline of the body from a lifted sideways (abducted) position and help stabilize the pelvis as you walk.
Hip Abductors (Gluteus Medius, Gluteus Minimus and Tensor Fasciae Latae) help lift the leg sideways, away from the midline of the body and help stabilize the pelvis as you walk.
Core Muscles
Abdominals (rectus abdominis, transverse abdominis, obliques) help stabilize your torso and maintain posture.
Lower back muscles (extensors, flexors, and oblique muscles) provide spinal support and help maintain balance.
Arm and Shoulder Muscles (Deltoids, biceps, and triceps) are also slightly engaged if you swing your arms naturally or walk with weights in your hands.
Walking briskly (4.5 to 6 km per hour) with good posture, including some stretch of upward slopes in your walk, increasing walking pace or light jogging in intervals, consciously engaging your core (below the naval) muscles and pumping arms as you walk help improve muscle tone.
Also read ‘Magical Health Benefits Of Walking’ and ‘Walking To Be Slim And Healthy’ on this website
Medium
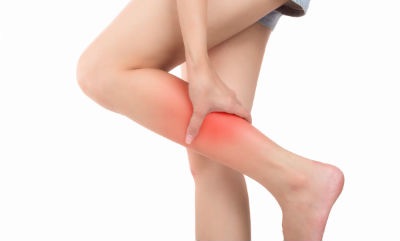
Muscle Cramps, A Common Problem!
Sudden, Painful Spasms Of Muscles!
Muscle cramps is a sudden and very painful condition that most people have experienced some time or another in their lives.
Muscle cramps means a sudden, involuntary and very painful contraction of a muscle or a group of muscles that actually freezes a person in that position, making it very difficult to move.
Such cramps are more common in the calf muscles and occur more often at night, but cramps can occur in other muscles and anytime of the day too.
Common Causes of Muscle Cramps
Dehydration:
Loss of fluids through sweating or inadequate intake of water can disturb electrolyte balance.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Low levels of magnesium, potassium, calcium, or sodium can trigger cramps.
Overuse or Strain:
Prolonged exercise or muscle fatigue can lead to cramps, especially in hot weather.
Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Holding one position too long, particularly with legs bent or crossed.
Poor Circulation:
Reduced blood flow to muscles, especially in peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Nerve Compression:
Spinal nerve issues (like lumbar stenosis) can cause cramping pain, especially in legs.
Medications:
Diuretics, statins, or certain blood pressure medications can cause cramps.
Medical Conditions:
Diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, or liver cirrhosis.
Pregnancy:
Common in the second and third trimesters due to changes in circulation and pressure on nerves.
Treatment and Relief
Immediate Relief:
Stretching and Massage
Gently stretch (e.g., flex the foot for a calf cramp) and massage the cramped muscle
Apply Heat or Cold:
Use heat (e.g., warm towel or heating pad) for tight muscles.
Apply ice packs for soreness of muscles after that comes after the cramp.
Hydration
Drink adequate water or an electrolyte drink, especially after sweating or exercise.
Long-Term Management & Prevention
Stay Well Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Correct Electrolyte Deficiencies:
Eat foods rich in potassium (bananas, oranges), magnesium (nuts, legumes), and calcium (milk, leafy greens).
Stretch Regularly:
Gentle stretches before bed, especially if you get night cramps.
Adjust Exercise Routine:
Avoid overtraining and allow time for rest and muscle recovery.
Use Proper Footwear:
Use supportive shoes, especially if you’re on your feet a lot.
Medication Review:
Consult your doctor if cramps persist, or if they started after a new medication.
Also read the article ‘Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!’ on this website.
Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Occasional Fatigue And Pain In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Many regular walkers experience days of weakness, fatigue or heaviness and pain in legs when they wake up in the morning and want to go out for their regular walk.
It could happen due to a few reasons, mostly not too serious.
Sweating heavily on long walks especially on warm and humid days and not drinking enough water can cause dehydration which can cause interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles causing this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Same kind of interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles can occur due to the deficiency of magnesium, potassium or calcium and can cause this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Repetitive use of quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles in walking sometimes can cause building up of lactic acid in these muscle groups or can cause micro tears in muscles, causing heaviness or drained feeling in these muscles. This happens more often if you have increased the intensity or duration of walks or have added some upward slopes in walks recently.
This can also happen if the muscles haven’t gotten enough time to recover from long walks or prolonged standing.
This can also happen if your shoes do not provide proper support to the arch of your feet or if the sole of your shoes have worn thin with long use, or you have been walking on hard surfaces, causing strain on your leg muscles, making them painful.
Pain in legs could also be caused by vertebral problems causing pressure on the nerves going down into the legs or due to some neurological diseases, but these pains are less likely to be temporary.
Preventive tips:
Drink ample water, more so in hot climates.
Use good quality walking shoes of a good brand.
Try walking on softer surfaces like on natural ground or lawns.
Lie on your bed with your legs elevated, preferably against a wall close to the bed, or on cushions or roll of a blanket, after a walk.
Have a rest day between walking days to allow the muscles to ‘recover’.
Include magnesium rich foods like pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, almonds, cashew nuts (in moderation if you’re watching your weight), brown rice, oats, black , lentils (masur, toor, mug, matki), chickpeas, soya, spinach and other green leafy vegetables, sea fish, in your food.
Happy walking to all!
Also read ‘Magical Health Benefits Of Walking’ and ‘Walking To Be Slim And Healthy’ on this website!
Large
Muscle Cramps, A Common Problem!
Sudden, Painful Spasms Of Muscles!
Muscle cramps is a sudden and very painful condition that most people have experienced some time or another in their lives.
Muscle cramps means a sudden, involuntary and very painful contraction of a muscle or a group of muscles that actually freezes a person in that position, making it very difficult to move.
Such cramps are more common in the calf muscles and occur more often at night, but cramps can occur in other muscles and anytime of the day too.
Common Causes of Muscle Cramps
Dehydration:
Loss of fluids through sweating or inadequate intake of water can disturb electrolyte balance.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Low levels of magnesium, potassium, calcium, or sodium can trigger cramps.
Overuse or Strain:
Prolonged exercise or muscle fatigue can lead to cramps, especially in hot weather.
Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Holding one position too long, particularly with legs bent or crossed.
Poor Circulation:
Reduced blood flow to muscles, especially in peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Nerve Compression:
Spinal nerve issues (like lumbar stenosis) can cause cramping pain, especially in legs.
Medications:
Diuretics, statins, or certain blood pressure medications can cause cramps.
Medical Conditions:
Diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, or liver cirrhosis.
Pregnancy:
Common in the second and third trimesters due to changes in circulation and pressure on nerves.
Treatment and Relief
Immediate Relief:
Stretching and Massage
Gently stretch (e.g., flex the foot for a calf cramp) and massage the cramped muscle
Apply Heat or Cold:
Use heat (e.g., warm towel or heating pad) for tight muscles.
Apply ice packs for soreness of muscles after that comes after the cramp.
Hydration
Drink adequate water or an electrolyte drink, especially after sweating or exercise.
Long-Term Management & Prevention
Stay Well Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Correct Electrolyte Deficiencies:
Eat foods rich in potassium (bananas, oranges), magnesium (nuts, legumes), and calcium (milk, leafy greens).
Stretch Regularly:
Gentle stretches before bed, especially if you get night cramps.
Adjust Exercise Routine:
Avoid overtraining and allow time for rest and muscle recovery.
Use Proper Footwear:
Use supportive shoes, especially if you’re on your feet a lot.
Medication Review:
Consult your doctor if cramps persist, or if they started after a new medication.
Also read the article ‘Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!’ on this website.
Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Occasional Fatigue And Pain In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Many regular walkers experience days of weakness, fatigue or heaviness and pain in legs when they wake up in the morning and want to go out for their regular walk.
It could happen due to a few reasons, mostly not too serious.
Sweating heavily on long walks especially on warm and humid days and not drinking enough water can cause dehydration which can cause interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles causing this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Same kind of interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles can occur due to the deficiency of magnesium, potassium or calcium and can cause this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Repetitive use of quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles in walking sometimes can cause building up of lactic acid in these muscle groups or can cause micro tears in muscles, causing heaviness or drained feeling in these muscles. This happens more often if you have increased the intensity or duration of walks or have added some upward slopes in walks recently.
This can also happen if the muscles haven’t gotten enough time to recover from long walks or prolonged standing.
This can also happen if your shoes do not provide proper support to the arch of your feet or if the sole of your shoes have worn thin with long use, or you have been walking on hard surfaces, causing strain on your leg muscles, making them painful.
Pain in legs could also be caused by vertebral problems causing pressure on the nerves going down into the legs or due to some neurological diseases, but these pains are less likely to be temporary.
Preventive tips:
Drink ample water, more so in hot climates.
Use good quality walking shoes of a good brand.
Try walking on softer surfaces like on natural ground or lawns.
Lie on your bed with your legs elevated, preferably against a wall close to the bed, or on cushions or roll of a blanket, after a walk.
Have a rest day between walking days to allow the muscles to ‘recover’.
Include magnesium rich foods like pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, almonds, cashew nuts (in moderation if you’re watching your weight), brown rice, oats, black , lentils (masur, toor, mug, matki), chickpeas, soya, spinach and other green leafy vegetables, sea fish, in your food.
Happy walking to all!
Also read ‘Magical Health Benefits Of Walking’ and ‘Walking To Be Slim And Healthy’ on this website!
Large Alt
Muscle Cramps, A Common Problem!
Sudden, Painful Spasms Of Muscles!
Muscle cramps is a sudden and very painful condition that most people have experienced some time or another in their lives.
Muscle cramps means a sudden, involuntary and very painful contraction of a muscle or a group of muscles that actually freezes a person in that position, making it very difficult to move.
Such cramps are more common in the calf muscles and occur more often at night, but cramps can occur in other muscles and anytime of the day too.
Common Causes of Muscle Cramps
Dehydration:
Loss of fluids through sweating or inadequate intake of water can disturb electrolyte balance.
Electrolyte Imbalance:
Low levels of magnesium, potassium, calcium, or sodium can trigger cramps.
Overuse or Strain:
Prolonged exercise or muscle fatigue can lead to cramps, especially in hot weather.
Prolonged Sitting or Standing:
Holding one position too long, particularly with legs bent or crossed.
Poor Circulation:
Reduced blood flow to muscles, especially in peripheral artery disease (PAD).
Nerve Compression:
Spinal nerve issues (like lumbar stenosis) can cause cramping pain, especially in legs.
Medications:
Diuretics, statins, or certain blood pressure medications can cause cramps.
Medical Conditions:
Diabetes, kidney disease, thyroid disorders, or liver cirrhosis.
Pregnancy:
Common in the second and third trimesters due to changes in circulation and pressure on nerves.
Treatment and Relief
Immediate Relief:
Stretching and Massage
Gently stretch (e.g., flex the foot for a calf cramp) and massage the cramped muscle
Apply Heat or Cold:
Use heat (e.g., warm towel or heating pad) for tight muscles.
Apply ice packs for soreness of muscles after that comes after the cramp.
Hydration
Drink adequate water or an electrolyte drink, especially after sweating or exercise.
Long-Term Management & Prevention
Stay Well Hydrated:
Drink plenty of water throughout the day.
Correct Electrolyte Deficiencies:
Eat foods rich in potassium (bananas, oranges), magnesium (nuts, legumes), and calcium (milk, leafy greens).
Stretch Regularly:
Gentle stretches before bed, especially if you get night cramps.
Adjust Exercise Routine:
Avoid overtraining and allow time for rest and muscle recovery.
Use Proper Footwear:
Use supportive shoes, especially if you’re on your feet a lot.
Medication Review:
Consult your doctor if cramps persist, or if they started after a new medication.
Also read the article ‘Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!’ on this website.
Occasional Heaviness Or Weakness In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Occasional Fatigue And Pain In Legs Of Regular Walkers!
Many regular walkers experience days of weakness, fatigue or heaviness and pain in legs when they wake up in the morning and want to go out for their regular walk.
It could happen due to a few reasons, mostly not too serious.
Sweating heavily on long walks especially on warm and humid days and not drinking enough water can cause dehydration which can cause interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles causing this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Same kind of interference in normal contraction and relaxation of muscles can occur due to the deficiency of magnesium, potassium or calcium and can cause this kind of heaviness or fatigue in leg muscles.
Repetitive use of quadriceps, hamstrings and calf muscles in walking sometimes can cause building up of lactic acid in these muscle groups or can cause micro tears in muscles, causing heaviness or drained feeling in these muscles. This happens more often if you have increased the intensity or duration of walks or have added some upward slopes in walks recently.
This can also happen if the muscles haven’t gotten enough time to recover from long walks or prolonged standing.
This can also happen if your shoes do not provide proper support to the arch of your feet or if the sole of your shoes have worn thin with long use, or you have been walking on hard surfaces, causing strain on your leg muscles, making them painful.
Pain in legs could also be caused by vertebral problems causing pressure on the nerves going down into the legs or due to some neurological diseases, but these pains are less likely to be temporary.
Preventive tips:
Drink ample water, more so in hot climates.
Use good quality walking shoes of a good brand.
Try walking on softer surfaces like on natural ground or lawns.
Lie on your bed with your legs elevated, preferably against a wall close to the bed, or on cushions or roll of a blanket, after a walk.
Have a rest day between walking days to allow the muscles to ‘recover’.
Include magnesium rich foods like pumpkin seeds, chia seeds, almonds, cashew nuts (in moderation if you’re watching your weight), brown rice, oats, black , lentils (masur, toor, mug, matki), chickpeas, soya, spinach and other green leafy vegetables, sea fish, in your food.
Happy walking to all!
Also read ‘Magical Health Benefits Of Walking’ and ‘Walking To Be Slim And Healthy’ on this website!