Posts Shortcodes
You can show the posts with Porto Blog, Porto Recent Posts shortcodes.
Recent
Timeline
March 2026
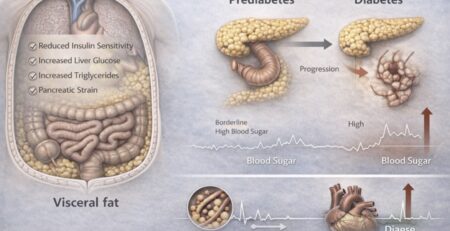
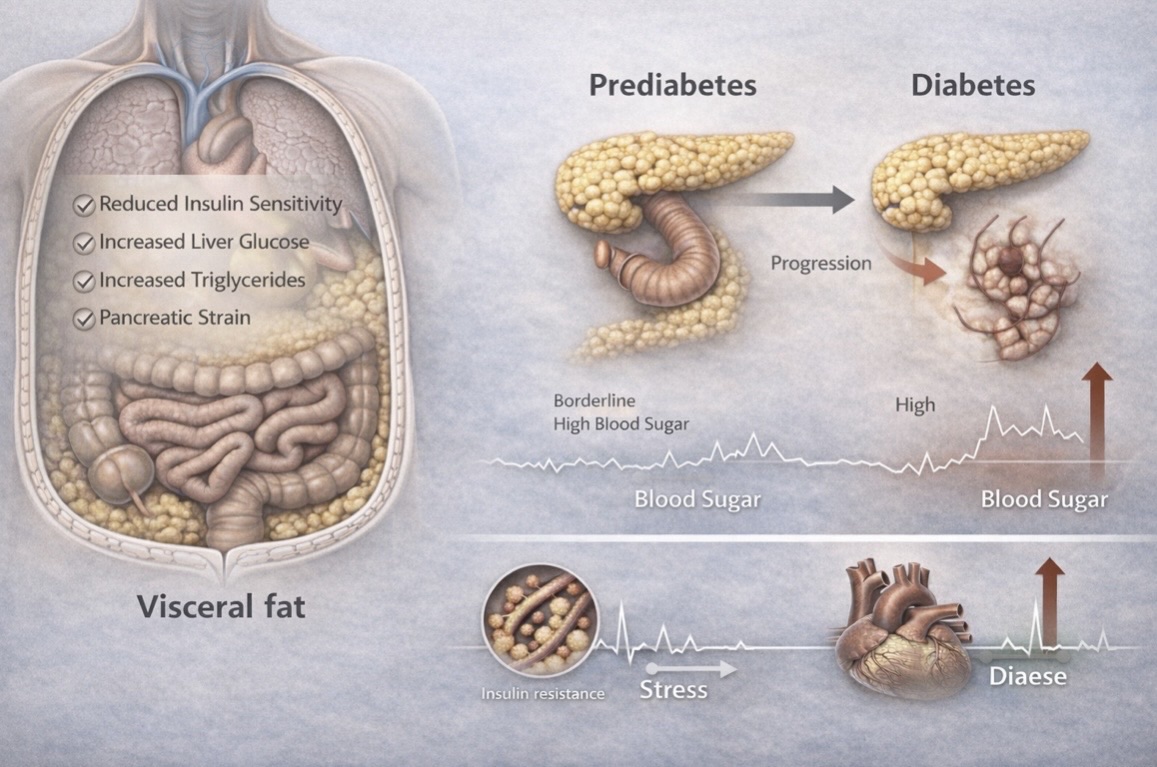
Visceral Fat, Pre Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
The Connection Between Visceral Fat, Pre diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
Type 2 diabetes does not appear suddenly.
It develops gradually — often over years — and visceral fat is at the centre of this process.
Understanding this connection is critical.
What Is Visceral Fat?
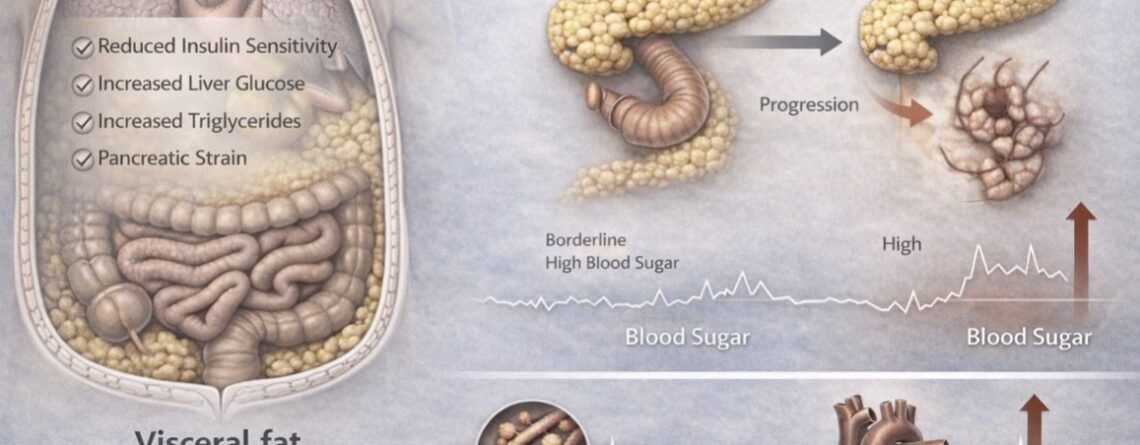
Visceral fat is the fat stored deep inside the abdomen, around the liver, pancreas and intestines.
Unlike the fat beneath the skin, visceral fat is metabolically active. It releases inflammatory substances and hormonal signals directly into the liver, promoting:
Insulin resistance
Increased glucose production
Higher triglycerides
Fatty liver
Systemic inflammation
It is not passive storage fat — it actively drives metabolic disease.
How It leads to pre diabetes:
When visceral fat increases, the liver and muscles become resistant to insulin, meaning their cells need more insulin to be able to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
The pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. For a time, blood sugar remains only mildly elevated. This stage is called pre diabetes.
Common early signs include:
Borderline fasting glucose
HbA1c in the pre diabetic range
Rising triglycerides
Increasing waist circumference
Most individuals feel completely well.
But internally, pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin are under strain.
If visceral fat continues to accumulate, compensation fails — and pre diabetes progresses to type 2 diabetes.
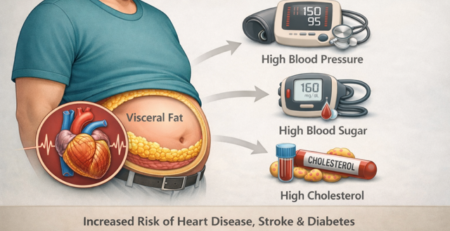
Why South Asians Are at Higher Risk
South Asians tend to develop visceral fat at lower Body Mass Index (BMI) levels.
A person may appear “normal weight” yet carry significant abdominal fat and insulin resistance.
Waist circumference is often a better indicator of risk:
Men: Above 90 cm
Women: Above 80 cm
It is not just how much you weigh — but where fat is stored that is important.
The Self-Perpetuating Cycle:
Greater the visceral fat, greater the insulin resistance,
Greater the insulin levels, greater the storage of visceral fat.
Chronic stress, inactivity, refined carbohydrates and poor sleep accelerate this cycle.
Over time, this leads to:
Persistent high blood sugar
High triglycerides
Low HDL cholesterol
Fatty liver
Hypertension
This cluster forms the basis of metabolic syndrome — with visceral fat as the driver.
The Encouraging Reality
Visceral fat responds well to lifestyle intervention.
Even a 5–7% reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Effective measures include:
Regular brisk walking
Resistance training
Reducing refined carbohydrates
Adequate protein intake
Good sleep
Stress management
When addressed early, pre diabetes can often be reversed.
Summary
Visceral fat is the main driver of insulin resistance.
Pre diabetes is a warning stage, not a harmless condition.
South Asians are vulnerable even at lower BMI levels.
Waist circumference is a powerful risk marker.
Early lifestyle correction can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Abdominal obesity is not merely cosmetic.
It is a metabolic warning sign.
Related article:
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
February 2026
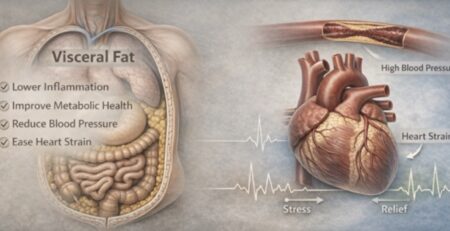
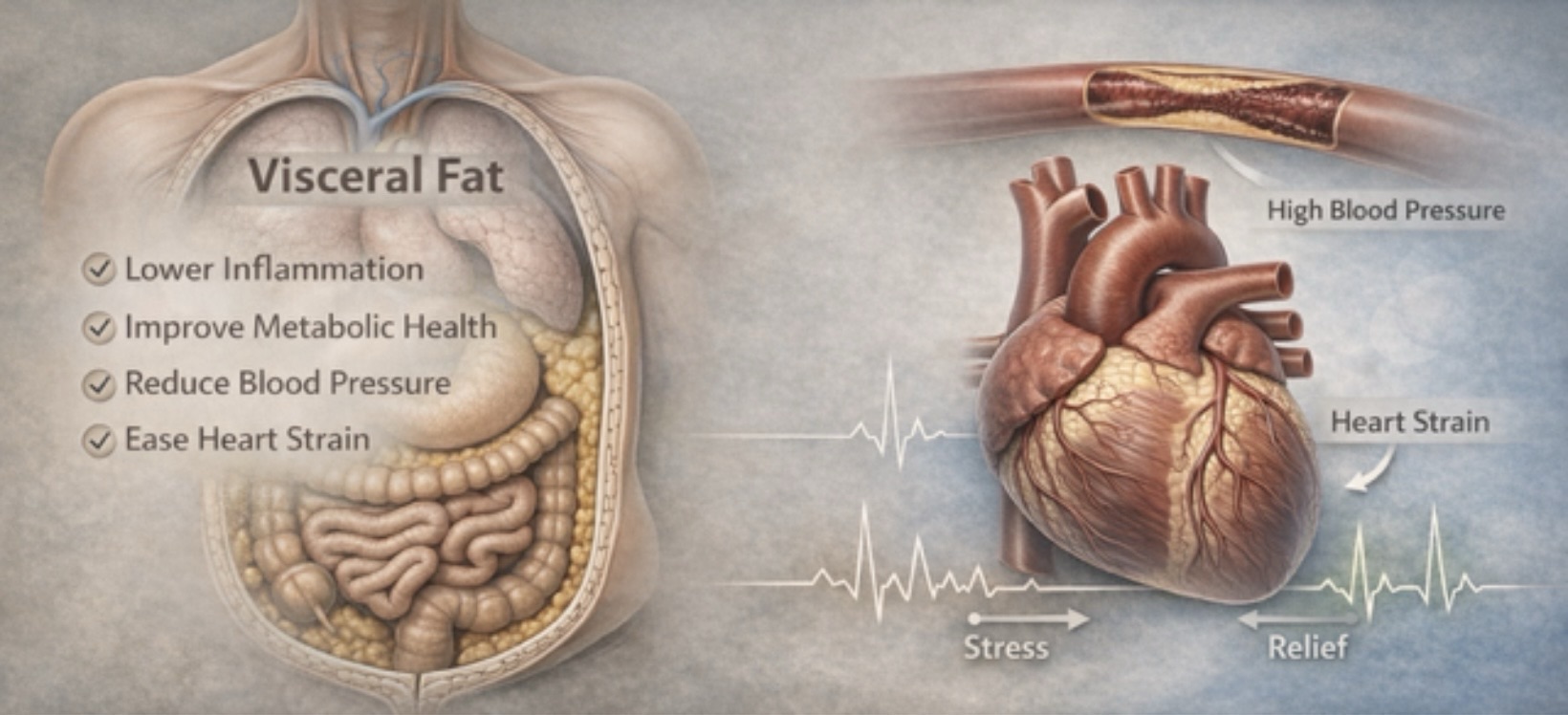
Visceral Fat And Heart Health!
The Relationship Of Abdominal Fat And Heart Health!
When the Belly Shrinks, the Heart Sighs in Relief
There is a visible change when abdominal girth reduces. Clothes fit better. Movement feels lighter. Energy improves.
But there is also an invisible change — deeper, quieter, far more important.
The heart’s workload begins to fall.
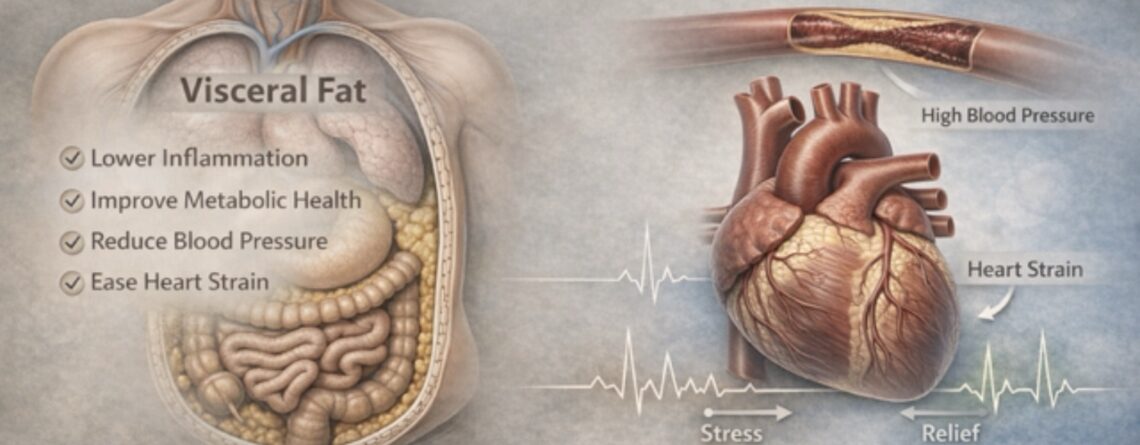
Visceral fat — the fat stored deep inside the abdomen around the liver, pancreas, and intestines — is not passive storage. It is biologically active tissue. It releases inflammatory chemicals, alters insulin sensitivity, increases blood pressure, and disrupts lipid metabolism.
It behaves less like stored fuel and more like an endocrine organ.
And the heart pays the price.
***
The Mechanical Burden
Every kilogram of excess tissue requires blood supply. More tissue means:
Greater total blood volume
Higher cardiac output
Increased pressure load
Thickening of the heart muscle over time
The heart must pump harder and more frequently to serve a larger metabolic territory.
When visceral fat reduces, circulating blood volume gradually decreases. Peripheral resistance improves. The demand on cardiac output falls. The heart can pump more efficiently, with less strain.
***
The Hormonal and Inflammatory Load
Visceral fat secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines and contributes to insulin resistance. This combination:
Stiffens arteries
Impairs endothelial function
Promotes plaque formation
Raises triglycerides
Lowers HDL cholesterol
Chronic low-grade inflammation keeps the vascular system in a constant state of irritation.
When visceral fat reduces, inflammatory markers like CRP often decline
Insulin sensitivity improves.
Blood pressure tends to fall
Lipid patterns shift favorably
The inner lining of the arteries — the endothelium — begins to function better.
Nitric oxide production improves
Arteries regain some of their flexibility.
And flexible arteries make the heart’s job easier.
***
The Blood Pressure Effect
Abdominal obesity is strongly linked with hypertension. Mechanisms include:
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
Increased renin-angiotensin activity
Sodium retention
Arterial stiffness
Reduction in visceral fat often leads to measurable drops in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Even a 5–10% reduction in body weight can produce meaningful cardiovascular benefits.
Lower pressure means less resistance
Less resistance means less strain
Less strain means reduced risk of heart failure, stroke, and coronary events.
***
The Metabolic Reset
Visceral fat is central to metabolic syndrome — the cluster of:
Elevated fasting glucose
High triglycerides
Low HDL
Hypertension
Central obesity
As abdominal fat reduces, this cluster begins to unravel.
Insulin works better
The liver produces fewer atherogenic particles
Triglycerides fall
HDL may rise
Glycemic variability decreases
Each of these changes independently reduces cardiovascular risk. Together, they compound.
***
Structural Changes in the Heart
Over time, excess weight can cause:
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Diastolic dysfunction
Enlargement of cardiac chambers
Weight and visceral fat reduction have been shown to partially reverse some of these structural changes, especially when achieved early.
The heart remodels in a favorable direction.
It is not just about prevention. It is about recovery.
***
Beyond Numbers
The tape measure tells one story.
The scale tells another.
But the more meaningful shift happens at the cellular and vascular level.
When visceral fat decreases:
The inflammatory storm quiets
Arterial walls relax
Blood pressure softens
Glucose control stabilizes
The heart pumps against less resistance
The change is systemic
The abdomen becomes smaller
The arteries become healthier
The heart becomes less burdened
And the risk curve bends downward.
***
A Practical Perspective
This is not about cosmetic weight loss.
It is about reducing metabolic load.
Waist circumference is often a more useful marker of cardiovascular risk than weight alone.
A gradual, sustained reduction through:
Balanced nutrition
Regular aerobic activity
Resistance training
Adequate sleep
Stress reduction can produce profound internal change — even before dramatic visual transformation occurs.
A shrinking waist is not vanity.
It is vascular protection.
Related articles:
‘Abdominal Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease’
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Grid
Visceral Fat, Pre Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
The Connection Between Visceral Fat, Pre diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
Type 2 diabetes does not appear suddenly.
It develops gradually — often over years — and visceral fat is at the centre of this process.
Understanding this connection is critical.
What Is Visceral Fat?
Visceral fat is the fat stored deep inside the abdomen, around the liver, pancreas and intestines.
Unlike the fat beneath the skin, visceral fat is metabolically active. It releases inflammatory substances and hormonal signals directly into the liver, promoting:
Insulin resistance
Increased glucose production
Higher triglycerides
Fatty liver
Systemic inflammation
It is not passive storage fat — it actively drives metabolic disease.
How It leads to pre diabetes:
When visceral fat increases, the liver and muscles become resistant to insulin, meaning their cells need more insulin to be able to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
The pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. For a time, blood sugar remains only mildly elevated. This stage is called pre diabetes.
Common early signs include:
Borderline fasting glucose
HbA1c in the pre diabetic range
Rising triglycerides
Increasing waist circumference
Most individuals feel completely well.
But internally, pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin are under strain.
If visceral fat continues to accumulate, compensation fails — and pre diabetes progresses to type 2 diabetes.
Why South Asians Are at Higher Risk
South Asians tend to develop visceral fat at lower Body Mass Index (BMI) levels.
A person may appear “normal weight” yet carry significant abdominal fat and insulin resistance.
Waist circumference is often a better indicator of risk:
Men: Above 90 cm
Women: Above 80 cm
It is not just how much you weigh — but where fat is stored that is important.
The Self-Perpetuating Cycle:
Greater the visceral fat, greater the insulin resistance,
Greater the insulin levels, greater the storage of visceral fat.
Chronic stress, inactivity, refined carbohydrates and poor sleep accelerate this cycle.
Over time, this leads to:
Persistent high blood sugar
High triglycerides
Low HDL cholesterol
Fatty liver
Hypertension
This cluster forms the basis of metabolic syndrome — with visceral fat as the driver.
The Encouraging Reality
Visceral fat responds well to lifestyle intervention.
Even a 5–7% reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Effective measures include:
Regular brisk walking
Resistance training
Reducing refined carbohydrates
Adequate protein intake
Good sleep
Stress management
When addressed early, pre diabetes can often be reversed.
Summary
Visceral fat is the main driver of insulin resistance.
Pre diabetes is a warning stage, not a harmless condition.
South Asians are vulnerable even at lower BMI levels.
Waist circumference is a powerful risk marker.
Early lifestyle correction can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Abdominal obesity is not merely cosmetic.
It is a metabolic warning sign.
Related article:
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Visceral Fat And Heart Health!
The Relationship Of Abdominal Fat And Heart Health!
When the Belly Shrinks, the Heart Sighs in Relief
There is a visible change when abdominal girth reduces. Clothes fit better. Movement feels lighter. Energy improves.
But there is also an invisible change — deeper, quieter, far more important.
The heart’s workload begins to fall.
Visceral fat — the fat stored deep inside the abdomen around the liver, pancreas, and intestines — is not passive storage. It is biologically active tissue. It releases inflammatory chemicals, alters insulin sensitivity, increases blood pressure, and disrupts lipid metabolism.
It behaves less like stored fuel and more like an endocrine organ.
And the heart pays the price.
***
The Mechanical Burden
Every kilogram of excess tissue requires blood supply. More tissue means:
Greater total blood volume
Higher cardiac output
Increased pressure load
Thickening of the heart muscle over time
The heart must pump harder and more frequently to serve a larger metabolic territory.
When visceral fat reduces, circulating blood volume gradually decreases. Peripheral resistance improves. The demand on cardiac output falls. The heart can pump more efficiently, with less strain.
***
The Hormonal and Inflammatory Load
Visceral fat secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines and contributes to insulin resistance. This combination:
Stiffens arteries
Impairs endothelial function
Promotes plaque formation
Raises triglycerides
Lowers HDL cholesterol
Chronic low-grade inflammation keeps the vascular system in a constant state of irritation.
When visceral fat reduces, inflammatory markers like CRP often decline
Insulin sensitivity improves.
Blood pressure tends to fall
Lipid patterns shift favorably
The inner lining of the arteries — the endothelium — begins to function better.
Nitric oxide production improves
Arteries regain some of their flexibility.
And flexible arteries make the heart’s job easier.
***
The Blood Pressure Effect
Abdominal obesity is strongly linked with hypertension. Mechanisms include:
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
Increased renin-angiotensin activity
Sodium retention
Arterial stiffness
Reduction in visceral fat often leads to measurable drops in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Even a 5–10% reduction in body weight can produce meaningful cardiovascular benefits.
Lower pressure means less resistance
Less resistance means less strain
Less strain means reduced risk of heart failure, stroke, and coronary events.
***
The Metabolic Reset
Visceral fat is central to metabolic syndrome — the cluster of:
Elevated fasting glucose
High triglycerides
Low HDL
Hypertension
Central obesity
As abdominal fat reduces, this cluster begins to unravel.
Insulin works better
The liver produces fewer atherogenic particles
Triglycerides fall
HDL may rise
Glycemic variability decreases
Each of these changes independently reduces cardiovascular risk. Together, they compound.
***
Structural Changes in the Heart
Over time, excess weight can cause:
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Diastolic dysfunction
Enlargement of cardiac chambers
Weight and visceral fat reduction have been shown to partially reverse some of these structural changes, especially when achieved early.
The heart remodels in a favorable direction.
It is not just about prevention. It is about recovery.
***
Beyond Numbers
The tape measure tells one story.
The scale tells another.
But the more meaningful shift happens at the cellular and vascular level.
When visceral fat decreases:
The inflammatory storm quiets
Arterial walls relax
Blood pressure softens
Glucose control stabilizes
The heart pumps against less resistance
The change is systemic
The abdomen becomes smaller
The arteries become healthier
The heart becomes less burdened
And the risk curve bends downward.
***
A Practical Perspective
This is not about cosmetic weight loss.
It is about reducing metabolic load.
Waist circumference is often a more useful marker of cardiovascular risk than weight alone.
A gradual, sustained reduction through:
Balanced nutrition
Regular aerobic activity
Resistance training
Adequate sleep
Stress reduction can produce profound internal change — even before dramatic visual transformation occurs.
A shrinking waist is not vanity.
It is vascular protection.
Related articles:
‘Abdominal Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease’
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
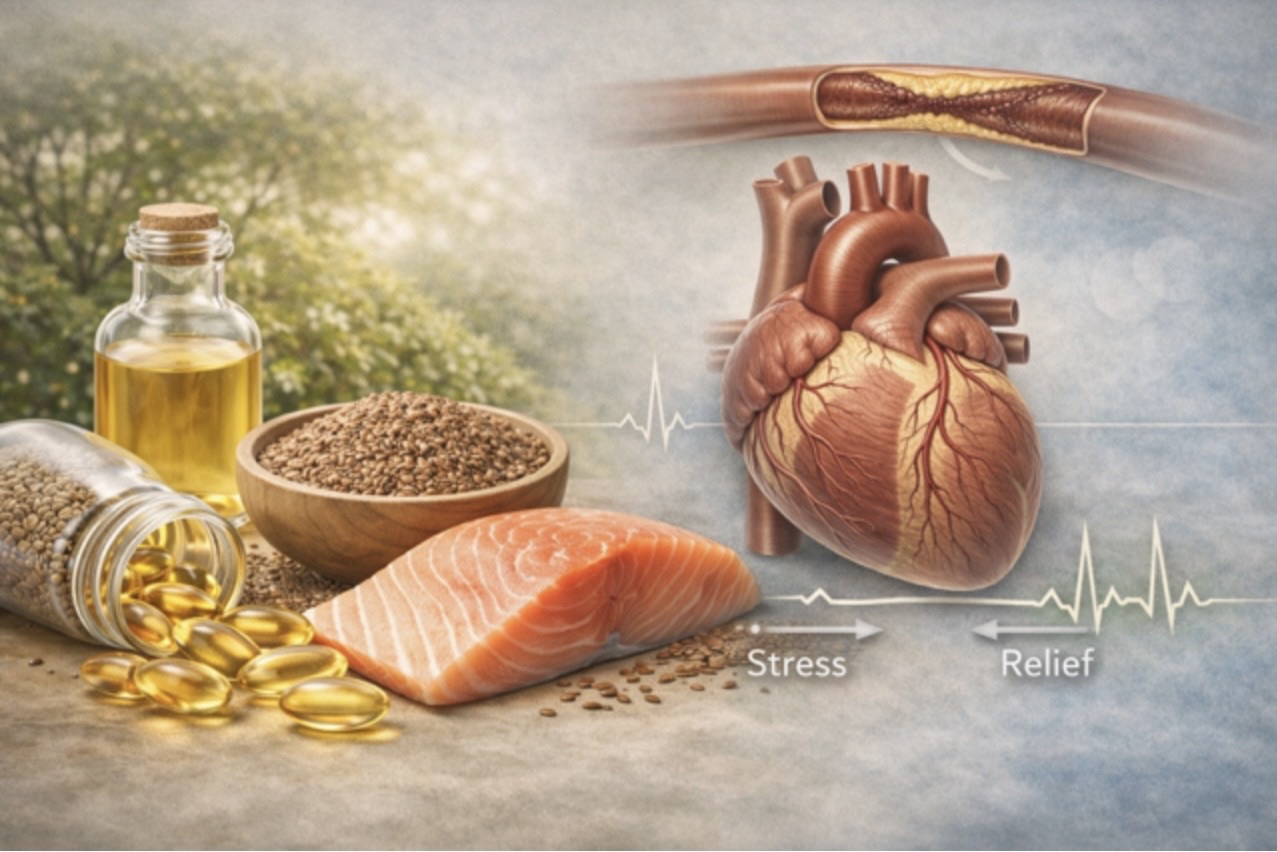
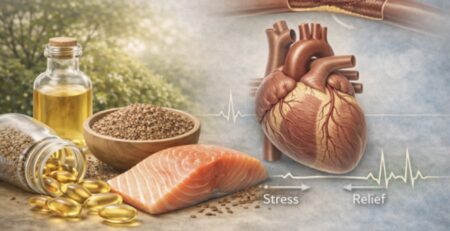
Omega 3 And Heart Health
Omega-3 Fatty Acids, Nitric Oxide And Vascular Health
Omega-3 fatty acids have earned their place in heart health for good reason. Their benefits go far beyond “reducing cholesterol.” In fact, their most powerful effects occur within the delicate inner lining of our blood vessels — the endothelium.
The endothelium is not merely a passive lining. It is a living, active tissue that constantly works to keep blood flowing smoothly. One of its most important functions is the production of nitric oxide.
Nitric oxide is a tiny gas molecule, yet its impact on cardiovascular health is enormous. It relaxes blood vessels, maintains their flexibility, improves blood flow, reduces unnecessary clot formation, lowers inflammation within the vessel wall, and helps slow the development of atherosclerosis. When nitric oxide production is healthy, arteries remain soft, elastic, and responsive.
How Omega-3 Supports Nitric Oxide
Omega-3 fatty acids, particularly EPA and DHA, support this process in multiple ways.
First, they become incorporated into the cell membranes of the endothelium. When these cell membranes are healthy and flexible, the cells function more efficiently. This improves the activity of the enzyme responsible for producing nitric oxide, allowing blood vessels to relax more effectively and helping maintain healthy blood pressure.
Second, omega-3 fatty acids reduce inflammation. Modern cardiovascular disease is not simply a matter of cholesterol deposition. It is largely driven by chronic inflammation within the arterial wall. Omega-3 fatty acids help calm this inflammation and support the body’s natural resolution processes. When inflammation is reduced, the endothelium functions better and nitric oxide production improves.
Third, omega-3 fatty acids reduce oxidative stress. Oxidative stress can rapidly destroy nitric oxide once it is formed. By lowering oxidative stress, omega-3 fatty acids help preserve nitric oxide, supporting better vascular tone and overall arterial health.
Additional Cardiovascular Benefits
Omega-3 fatty acids also reduce triglyceride levels, stabilise heart cell membranes, lower the tendency of blood to clot unnecessarily, and help maintain stable heart rhythm. They contribute to making existing arterial plaques more stable. A stable plaque is far less likely to rupture and trigger a heart attack or stroke.
This combination of improved endothelial function, reduced inflammation, lower oxidative stress, and plaque stability explains why adequate omega-3 intake is consistently associated with better cardiovascular outcomes.
What If One Does Not Eat Sea Fish?
Sea fish such as salmon, sardines or ‘tarli’, mackerel or ‘bangda’, Indian Salman or rawas, hilsa, king fish or ‘surmai’, pomfret, halva and rohu provide EPA and DHA in their ready-to-use form. However, many individuals do not consume sea fish regularly due to dietary preference, availability, or cultural patterns.
Compensation is possible.
Plant sources such as flaxseed, chia seeds, walnuts and mustard seeds provide alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), a plant-based omega-3 fatty acid. The body can convert ALA into EPA and DHA, although the conversion is limited. Even so, regular intake of ALA contributes meaningfully to cardiovascular protection and helps improve overall omega-3 balance.
For those who do not consume fish at all, algae-derived omega-3 supplements offer a practical solution. Algae are the original source of omega-3 in the marine food chain. Algal oil provides bioavailable DHA, and often EPA, without the need for fish consumption.
Restoring Balance
Modern diets often contain high amounts of refined vegetable oils rich in omega-6 fatty acids. Omega-6 fats are essential, but an excess relative to omega-3 may promote a pro-inflammatory environment. Improving omega-3 intake while moderating highly processed oils helps restore a healthier fatty acid balance within the body.
Lifestyle factors further amplify these benefits. Regular physical activity stimulates nitric oxide production. Reduction of visceral fat lowers inflammatory signalling. Adequate sleep and effective stress management are equally important, as chronic stress can impair nitric oxide availability and damage endothelial function.
The Larger Perspective
Omega-3 fatty acids are not a magic solution. They work best as part of a balanced lifestyle. However, when consistently included in the diet — whether through sea fish, plant sources, or algae-based supplements — they support nitric oxide production, reduce inflammation and oxidative stress, lower triglycerides, stabilise plaques, and help preserve vascular flexibility.
At its core, the story of omega-3 is a story of maintaining balance within the arteries — keeping them relaxed, resilient and functional over decades of life.
Also read articles, ‘Basics Of Nutrition’ and ‘Omega 3 Fatty Acids’ and ‘Effects Of Cooking On Omega 3 In Fish’ on this website.
Medium
Visceral Fat, Pre Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
The Connection Between Visceral Fat, Pre diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
Type 2 diabetes does not appear suddenly.
It develops gradually — often over years — and visceral fat is at the centre of this process.
Understanding this connection is critical.
What Is Visceral Fat?
Visceral fat is the fat stored deep inside the abdomen, around the liver, pancreas and intestines.
Unlike the fat beneath the skin, visceral fat is metabolically active. It releases inflammatory substances and hormonal signals directly into the liver, promoting:
Insulin resistance
Increased glucose production
Higher triglycerides
Fatty liver
Systemic inflammation
It is not passive storage fat — it actively drives metabolic disease.
How It leads to pre diabetes:
When visceral fat increases, the liver and muscles become resistant to insulin, meaning their cells need more insulin to be able to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
The pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. For a time, blood sugar remains only mildly elevated. This stage is called pre diabetes.
Common early signs include:
Borderline fasting glucose
HbA1c in the pre diabetic range
Rising triglycerides
Increasing waist circumference
Most individuals feel completely well.
But internally, pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin are under strain.
If visceral fat continues to accumulate, compensation fails — and pre diabetes progresses to type 2 diabetes.
Why South Asians Are at Higher Risk
South Asians tend to develop visceral fat at lower Body Mass Index (BMI) levels.
A person may appear “normal weight” yet carry significant abdominal fat and insulin resistance.
Waist circumference is often a better indicator of risk:
Men: Above 90 cm
Women: Above 80 cm
It is not just how much you weigh — but where fat is stored that is important.
The Self-Perpetuating Cycle:
Greater the visceral fat, greater the insulin resistance,
Greater the insulin levels, greater the storage of visceral fat.
Chronic stress, inactivity, refined carbohydrates and poor sleep accelerate this cycle.
Over time, this leads to:
Persistent high blood sugar
High triglycerides
Low HDL cholesterol
Fatty liver
Hypertension
This cluster forms the basis of metabolic syndrome — with visceral fat as the driver.
The Encouraging Reality
Visceral fat responds well to lifestyle intervention.
Even a 5–7% reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Effective measures include:
Regular brisk walking
Resistance training
Reducing refined carbohydrates
Adequate protein intake
Good sleep
Stress management
When addressed early, pre diabetes can often be reversed.
Summary
Visceral fat is the main driver of insulin resistance.
Pre diabetes is a warning stage, not a harmless condition.
South Asians are vulnerable even at lower BMI levels.
Waist circumference is a powerful risk marker.
Early lifestyle correction can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Abdominal obesity is not merely cosmetic.
It is a metabolic warning sign.
Related article:
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Visceral Fat And Heart Health!
The Relationship Of Abdominal Fat And Heart Health!
When the Belly Shrinks, the Heart Sighs in Relief
There is a visible change when abdominal girth reduces. Clothes fit better. Movement feels lighter. Energy improves.
But there is also an invisible change — deeper, quieter, far more important.
The heart’s workload begins to fall.
Visceral fat — the fat stored deep inside the abdomen around the liver, pancreas, and intestines — is not passive storage. It is biologically active tissue. It releases inflammatory chemicals, alters insulin sensitivity, increases blood pressure, and disrupts lipid metabolism.
It behaves less like stored fuel and more like an endocrine organ.
And the heart pays the price.
***
The Mechanical Burden
Every kilogram of excess tissue requires blood supply. More tissue means:
Greater total blood volume
Higher cardiac output
Increased pressure load
Thickening of the heart muscle over time
The heart must pump harder and more frequently to serve a larger metabolic territory.
When visceral fat reduces, circulating blood volume gradually decreases. Peripheral resistance improves. The demand on cardiac output falls. The heart can pump more efficiently, with less strain.
***
The Hormonal and Inflammatory Load
Visceral fat secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines and contributes to insulin resistance. This combination:
Stiffens arteries
Impairs endothelial function
Promotes plaque formation
Raises triglycerides
Lowers HDL cholesterol
Chronic low-grade inflammation keeps the vascular system in a constant state of irritation.
When visceral fat reduces, inflammatory markers like CRP often decline
Insulin sensitivity improves.
Blood pressure tends to fall
Lipid patterns shift favorably
The inner lining of the arteries — the endothelium — begins to function better.
Nitric oxide production improves
Arteries regain some of their flexibility.
And flexible arteries make the heart’s job easier.
***
The Blood Pressure Effect
Abdominal obesity is strongly linked with hypertension. Mechanisms include:
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
Increased renin-angiotensin activity
Sodium retention
Arterial stiffness
Reduction in visceral fat often leads to measurable drops in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Even a 5–10% reduction in body weight can produce meaningful cardiovascular benefits.
Lower pressure means less resistance
Less resistance means less strain
Less strain means reduced risk of heart failure, stroke, and coronary events.
***
The Metabolic Reset
Visceral fat is central to metabolic syndrome — the cluster of:
Elevated fasting glucose
High triglycerides
Low HDL
Hypertension
Central obesity
As abdominal fat reduces, this cluster begins to unravel.
Insulin works better
The liver produces fewer atherogenic particles
Triglycerides fall
HDL may rise
Glycemic variability decreases
Each of these changes independently reduces cardiovascular risk. Together, they compound.
***
Structural Changes in the Heart
Over time, excess weight can cause:
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Diastolic dysfunction
Enlargement of cardiac chambers
Weight and visceral fat reduction have been shown to partially reverse some of these structural changes, especially when achieved early.
The heart remodels in a favorable direction.
It is not just about prevention. It is about recovery.
***
Beyond Numbers
The tape measure tells one story.
The scale tells another.
But the more meaningful shift happens at the cellular and vascular level.
When visceral fat decreases:
The inflammatory storm quiets
Arterial walls relax
Blood pressure softens
Glucose control stabilizes
The heart pumps against less resistance
The change is systemic
The abdomen becomes smaller
The arteries become healthier
The heart becomes less burdened
And the risk curve bends downward.
***
A Practical Perspective
This is not about cosmetic weight loss.
It is about reducing metabolic load.
Waist circumference is often a more useful marker of cardiovascular risk than weight alone.
A gradual, sustained reduction through:
Balanced nutrition
Regular aerobic activity
Resistance training
Adequate sleep
Stress reduction can produce profound internal change — even before dramatic visual transformation occurs.
A shrinking waist is not vanity.
It is vascular protection.
Related articles:
‘Abdominal Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease’
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Large
Visceral Fat, Pre Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
The Connection Between Visceral Fat, Pre diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
Type 2 diabetes does not appear suddenly.
It develops gradually — often over years — and visceral fat is at the centre of this process.
Understanding this connection is critical.
What Is Visceral Fat?
Visceral fat is the fat stored deep inside the abdomen, around the liver, pancreas and intestines.
Unlike the fat beneath the skin, visceral fat is metabolically active. It releases inflammatory substances and hormonal signals directly into the liver, promoting:
Insulin resistance
Increased glucose production
Higher triglycerides
Fatty liver
Systemic inflammation
It is not passive storage fat — it actively drives metabolic disease.
How It leads to pre diabetes:
When visceral fat increases, the liver and muscles become resistant to insulin, meaning their cells need more insulin to be able to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
The pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. For a time, blood sugar remains only mildly elevated. This stage is called pre diabetes.
Common early signs include:
Borderline fasting glucose
HbA1c in the pre diabetic range
Rising triglycerides
Increasing waist circumference
Most individuals feel completely well.
But internally, pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin are under strain.
If visceral fat continues to accumulate, compensation fails — and pre diabetes progresses to type 2 diabetes.
Why South Asians Are at Higher Risk
South Asians tend to develop visceral fat at lower Body Mass Index (BMI) levels.
A person may appear “normal weight” yet carry significant abdominal fat and insulin resistance.
Waist circumference is often a better indicator of risk:
Men: Above 90 cm
Women: Above 80 cm
It is not just how much you weigh — but where fat is stored that is important.
The Self-Perpetuating Cycle:
Greater the visceral fat, greater the insulin resistance,
Greater the insulin levels, greater the storage of visceral fat.
Chronic stress, inactivity, refined carbohydrates and poor sleep accelerate this cycle.
Over time, this leads to:
Persistent high blood sugar
High triglycerides
Low HDL cholesterol
Fatty liver
Hypertension
This cluster forms the basis of metabolic syndrome — with visceral fat as the driver.
The Encouraging Reality
Visceral fat responds well to lifestyle intervention.
Even a 5–7% reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Effective measures include:
Regular brisk walking
Resistance training
Reducing refined carbohydrates
Adequate protein intake
Good sleep
Stress management
When addressed early, pre diabetes can often be reversed.
Summary
Visceral fat is the main driver of insulin resistance.
Pre diabetes is a warning stage, not a harmless condition.
South Asians are vulnerable even at lower BMI levels.
Waist circumference is a powerful risk marker.
Early lifestyle correction can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Abdominal obesity is not merely cosmetic.
It is a metabolic warning sign.
Related article:
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Visceral Fat And Heart Health!
The Relationship Of Abdominal Fat And Heart Health!
When the Belly Shrinks, the Heart Sighs in Relief
There is a visible change when abdominal girth reduces. Clothes fit better. Movement feels lighter. Energy improves.
But there is also an invisible change — deeper, quieter, far more important.
The heart’s workload begins to fall.
Visceral fat — the fat stored deep inside the abdomen around the liver, pancreas, and intestines — is not passive storage. It is biologically active tissue. It releases inflammatory chemicals, alters insulin sensitivity, increases blood pressure, and disrupts lipid metabolism.
It behaves less like stored fuel and more like an endocrine organ.
And the heart pays the price.
***
The Mechanical Burden
Every kilogram of excess tissue requires blood supply. More tissue means:
Greater total blood volume
Higher cardiac output
Increased pressure load
Thickening of the heart muscle over time
The heart must pump harder and more frequently to serve a larger metabolic territory.
When visceral fat reduces, circulating blood volume gradually decreases. Peripheral resistance improves. The demand on cardiac output falls. The heart can pump more efficiently, with less strain.
***
The Hormonal and Inflammatory Load
Visceral fat secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines and contributes to insulin resistance. This combination:
Stiffens arteries
Impairs endothelial function
Promotes plaque formation
Raises triglycerides
Lowers HDL cholesterol
Chronic low-grade inflammation keeps the vascular system in a constant state of irritation.
When visceral fat reduces, inflammatory markers like CRP often decline
Insulin sensitivity improves.
Blood pressure tends to fall
Lipid patterns shift favorably
The inner lining of the arteries — the endothelium — begins to function better.
Nitric oxide production improves
Arteries regain some of their flexibility.
And flexible arteries make the heart’s job easier.
***
The Blood Pressure Effect
Abdominal obesity is strongly linked with hypertension. Mechanisms include:
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
Increased renin-angiotensin activity
Sodium retention
Arterial stiffness
Reduction in visceral fat often leads to measurable drops in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Even a 5–10% reduction in body weight can produce meaningful cardiovascular benefits.
Lower pressure means less resistance
Less resistance means less strain
Less strain means reduced risk of heart failure, stroke, and coronary events.
***
The Metabolic Reset
Visceral fat is central to metabolic syndrome — the cluster of:
Elevated fasting glucose
High triglycerides
Low HDL
Hypertension
Central obesity
As abdominal fat reduces, this cluster begins to unravel.
Insulin works better
The liver produces fewer atherogenic particles
Triglycerides fall
HDL may rise
Glycemic variability decreases
Each of these changes independently reduces cardiovascular risk. Together, they compound.
***
Structural Changes in the Heart
Over time, excess weight can cause:
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Diastolic dysfunction
Enlargement of cardiac chambers
Weight and visceral fat reduction have been shown to partially reverse some of these structural changes, especially when achieved early.
The heart remodels in a favorable direction.
It is not just about prevention. It is about recovery.
***
Beyond Numbers
The tape measure tells one story.
The scale tells another.
But the more meaningful shift happens at the cellular and vascular level.
When visceral fat decreases:
The inflammatory storm quiets
Arterial walls relax
Blood pressure softens
Glucose control stabilizes
The heart pumps against less resistance
The change is systemic
The abdomen becomes smaller
The arteries become healthier
The heart becomes less burdened
And the risk curve bends downward.
***
A Practical Perspective
This is not about cosmetic weight loss.
It is about reducing metabolic load.
Waist circumference is often a more useful marker of cardiovascular risk than weight alone.
A gradual, sustained reduction through:
Balanced nutrition
Regular aerobic activity
Resistance training
Adequate sleep
Stress reduction can produce profound internal change — even before dramatic visual transformation occurs.
A shrinking waist is not vanity.
It is vascular protection.
Related articles:
‘Abdominal Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease’
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Large Alt
Visceral Fat, Pre Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
The Connection Between Visceral Fat, Pre diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes!
Type 2 diabetes does not appear suddenly.
It develops gradually — often over years — and visceral fat is at the centre of this process.
Understanding this connection is critical.
What Is Visceral Fat?
Visceral fat is the fat stored deep inside the abdomen, around the liver, pancreas and intestines.
Unlike the fat beneath the skin, visceral fat is metabolically active. It releases inflammatory substances and hormonal signals directly into the liver, promoting:
Insulin resistance
Increased glucose production
Higher triglycerides
Fatty liver
Systemic inflammation
It is not passive storage fat — it actively drives metabolic disease.
How It leads to pre diabetes:
When visceral fat increases, the liver and muscles become resistant to insulin, meaning their cells need more insulin to be able to absorb glucose from the bloodstream.
The pancreas compensates by producing more insulin. For a time, blood sugar remains only mildly elevated. This stage is called pre diabetes.
Common early signs include:
Borderline fasting glucose
HbA1c in the pre diabetic range
Rising triglycerides
Increasing waist circumference
Most individuals feel completely well.
But internally, pancreatic beta cells which produce insulin are under strain.
If visceral fat continues to accumulate, compensation fails — and pre diabetes progresses to type 2 diabetes.
Why South Asians Are at Higher Risk
South Asians tend to develop visceral fat at lower Body Mass Index (BMI) levels.
A person may appear “normal weight” yet carry significant abdominal fat and insulin resistance.
Waist circumference is often a better indicator of risk:
Men: Above 90 cm
Women: Above 80 cm
It is not just how much you weigh — but where fat is stored that is important.
The Self-Perpetuating Cycle:
Greater the visceral fat, greater the insulin resistance,
Greater the insulin levels, greater the storage of visceral fat.
Chronic stress, inactivity, refined carbohydrates and poor sleep accelerate this cycle.
Over time, this leads to:
Persistent high blood sugar
High triglycerides
Low HDL cholesterol
Fatty liver
Hypertension
This cluster forms the basis of metabolic syndrome — with visceral fat as the driver.
The Encouraging Reality
Visceral fat responds well to lifestyle intervention.
Even a 5–7% reduction in body weight can significantly improve insulin sensitivity.
Effective measures include:
Regular brisk walking
Resistance training
Reducing refined carbohydrates
Adequate protein intake
Good sleep
Stress management
When addressed early, pre diabetes can often be reversed.
Summary
Visceral fat is the main driver of insulin resistance.
Pre diabetes is a warning stage, not a harmless condition.
South Asians are vulnerable even at lower BMI levels.
Waist circumference is a powerful risk marker.
Early lifestyle correction can prevent or delay type 2 diabetes.
Abdominal obesity is not merely cosmetic.
It is a metabolic warning sign.
Related article:
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.
Visceral Fat And Heart Health!
The Relationship Of Abdominal Fat And Heart Health!
When the Belly Shrinks, the Heart Sighs in Relief
There is a visible change when abdominal girth reduces. Clothes fit better. Movement feels lighter. Energy improves.
But there is also an invisible change — deeper, quieter, far more important.
The heart’s workload begins to fall.
Visceral fat — the fat stored deep inside the abdomen around the liver, pancreas, and intestines — is not passive storage. It is biologically active tissue. It releases inflammatory chemicals, alters insulin sensitivity, increases blood pressure, and disrupts lipid metabolism.
It behaves less like stored fuel and more like an endocrine organ.
And the heart pays the price.
***
The Mechanical Burden
Every kilogram of excess tissue requires blood supply. More tissue means:
Greater total blood volume
Higher cardiac output
Increased pressure load
Thickening of the heart muscle over time
The heart must pump harder and more frequently to serve a larger metabolic territory.
When visceral fat reduces, circulating blood volume gradually decreases. Peripheral resistance improves. The demand on cardiac output falls. The heart can pump more efficiently, with less strain.
***
The Hormonal and Inflammatory Load
Visceral fat secretes pro-inflammatory cytokines and contributes to insulin resistance. This combination:
Stiffens arteries
Impairs endothelial function
Promotes plaque formation
Raises triglycerides
Lowers HDL cholesterol
Chronic low-grade inflammation keeps the vascular system in a constant state of irritation.
When visceral fat reduces, inflammatory markers like CRP often decline
Insulin sensitivity improves.
Blood pressure tends to fall
Lipid patterns shift favorably
The inner lining of the arteries — the endothelium — begins to function better.
Nitric oxide production improves
Arteries regain some of their flexibility.
And flexible arteries make the heart’s job easier.
***
The Blood Pressure Effect
Abdominal obesity is strongly linked with hypertension. Mechanisms include:
Activation of the sympathetic nervous system
Increased renin-angiotensin activity
Sodium retention
Arterial stiffness
Reduction in visceral fat often leads to measurable drops in systolic and diastolic blood pressure.
Even a 5–10% reduction in body weight can produce meaningful cardiovascular benefits.
Lower pressure means less resistance
Less resistance means less strain
Less strain means reduced risk of heart failure, stroke, and coronary events.
***
The Metabolic Reset
Visceral fat is central to metabolic syndrome — the cluster of:
Elevated fasting glucose
High triglycerides
Low HDL
Hypertension
Central obesity
As abdominal fat reduces, this cluster begins to unravel.
Insulin works better
The liver produces fewer atherogenic particles
Triglycerides fall
HDL may rise
Glycemic variability decreases
Each of these changes independently reduces cardiovascular risk. Together, they compound.
***
Structural Changes in the Heart
Over time, excess weight can cause:
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Diastolic dysfunction
Enlargement of cardiac chambers
Weight and visceral fat reduction have been shown to partially reverse some of these structural changes, especially when achieved early.
The heart remodels in a favorable direction.
It is not just about prevention. It is about recovery.
***
Beyond Numbers
The tape measure tells one story.
The scale tells another.
But the more meaningful shift happens at the cellular and vascular level.
When visceral fat decreases:
The inflammatory storm quiets
Arterial walls relax
Blood pressure softens
Glucose control stabilizes
The heart pumps against less resistance
The change is systemic
The abdomen becomes smaller
The arteries become healthier
The heart becomes less burdened
And the risk curve bends downward.
***
A Practical Perspective
This is not about cosmetic weight loss.
It is about reducing metabolic load.
Waist circumference is often a more useful marker of cardiovascular risk than weight alone.
A gradual, sustained reduction through:
Balanced nutrition
Regular aerobic activity
Resistance training
Adequate sleep
Stress reduction can produce profound internal change — even before dramatic visual transformation occurs.
A shrinking waist is not vanity.
It is vascular protection.
Related articles:
‘Abdominal Obesity, Diabetes and Heart Disease’
‘Waist Size, Blood Pressure, Blood Sugar And Heart Health!’.